Purpose: Learn how to use migration history to control your database changes
1.Preparation for Setting Entity Framework, connection string, and relating database
project -> right click ->
Properties
Then you can select the
relating database to this project.
2. Create Model and setup DbContext
a. Create a class which represents your table (Under Models folder).
For example, if we want to create a Person table, you can setup it as the following picture.
Note: Property name ends with Id will be considered as primary key in table.
Note: We use DbContext to coordinate Entity Framework Functionality.
In addition, add the previous class to DbSet.
Also, we can specific the database from customized connection string name.
On
this example, we named it “DefaultContext”
3. Migration
Tools -> NuGet Package Manager -> Package Manager Console
Run: enable-migrations
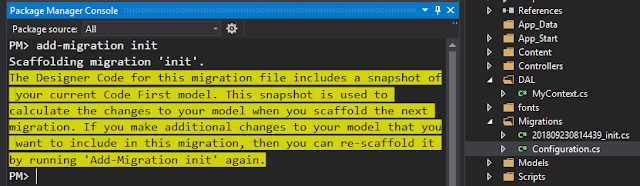
c. Run: “add-migration init” for creating migration
Note: "init" is the migration name in this example, you can use anything you want.
After that, we can see that under the folder, the migration file called “xxxx_init.cs” was created
Then, we can run "update-database" commands to change database.
d. On SQL Server management, we can find that the Person table was created!
In addition, this database includes the migration history table (Only One record.)
4. How to revert migrations
For testing purpose in this example, in this step, we want to deliberately make a mistake for the typo issue. And do the Migration to update database!
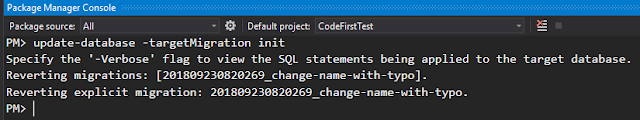
We can run the following commands on Console to revert to the specific migration history record.
Commands: update-databse -targetMigration init
d. Then we can find that the database has been reverted to the first migration we created before. And the second migration history has been removed!
e. Now, we can delete the wrong migration on our project folder.
e. Now, we can delete the wrong migration on our project folder.
Then, we correct the properties of models (correct the typo).




















No comments:
Post a Comment